
Mining, or the extraction of digital currencies, is one of the most popular ways to generate income. Unlike trading or investing, it does not require specific technical knowledge or in-depth expertise in the field of cryptocurrencies. For this reason, many users attempt to earn money through mining in hopes of making “easy” money.
However, the process is not as simple as it may seem. Cryptocurrency mining is becoming increasingly complex, while the reward for each mined block is gradually decreasing. This is due to the fact that most cryptocurrencies have a built-in deflationary mechanism in their code, which helps regulate both the currency’s value and the amount in circulation.
As mining conditions become more demanding, miners are forced to employ various strategies to maintain profitability. Some join forces to create mining pools, while others rent computing power from large data centers, among other methods. In this article, we will discuss in detail what mining is and how it can be done.
How cryptocurrency enters circulation
In the case of traditional money, its issuance is carried out by designated state authorities, usually central banks (CBs). In addition to issuance, CBs also regulate the circulation of money and may conduct additional emissions if necessary.
Governments can print money indefinitely, as its issuance is not restricted. This often leads to inflation, meaning a decrease in the currency's purchasing power. On the other hand, if the amount of money in circulation is insufficient, this reduces demand for goods and services and slows down production volumes.
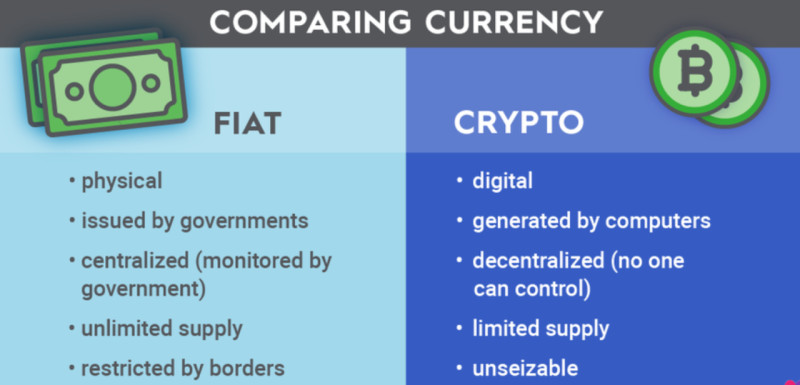
Digital money operates under entirely different principles. Firstly, most cryptocurrencies have a predetermined emission limit, and in some cases, a specific time frame within which the emission must be completed. This means that only a limited number of coins can enter circulation.
Secondly, the mechanisms of emission are also different. Additional units of a given currency do not simply enter the system; they must be mined. Thus, the process of issuing new coins is continuous and is directly tied to the operation of the network, that is, the blockchain.
How does blockchain work? Blockchain functions as a distributed ledger in which all operations conducted on the network are recorded. These records are grouped into blocks, and the blocks are linked together in a single chain, known as the blockchain. Each block is connected to the one before it, with every subsequent block containing a reference to its predecessor.
This structure enhances security: altering even a single transaction or block is impossible without changing all the preceding ones. Moreover, in order to add a transaction to a block, complex mathematical calculations must be performed—this is the process known as mining.
Mining algorithms
Currently, there are two most widely used mining algorithms: PoW (Proof of Work) and PoS (Proof of Stake), as well as some of their variations. Therefore, before understanding how mining works, it is important to determine in which networks and under what conditions it can be applied.
A brief comparison of these two algorithms is presented in the table below:
| Parameter | PoW | PoS |
| Equipment | Required | Not required |
| Energy consumption | High | Low |
| Method of transaction verification | Performing complex calculations | Staking tokens |
| Collateral participation | No | Yes |
| Reward for participation | Yes | Yes |
| Security | High | Low |
| Name of participants | Miners | Validators |
| Example cryptocurrencies | Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin | Solana, Cardano, Polygon |
Now, let us take a closer look at these algorithms. The first thing to understand is that any blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores data. However, this data is not stored on a single central server but across multiple devices that are not interconnected.
This architecture increases network security because in order to hack a blockchain, one would need to gain control over more than 51% of the devices, which is practically impossible. However, since transactions are verified and added to the chain by different devices, they need to reach an agreement regarding all the records in the ledger.
This agreement is achieved through the above-mentioned algorithms — Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). In the first case, adding a transaction requires solving a complex mathematical problem using specialized equipment. This task is performed by miners.
The one who finds the solution first receives a reward in the form of new currency units. Once the solution is found, it is sent by the miner to other network participants for verification. In this way, consensus is achieved in the chain, meaning that an identical copy of the ledger is stored on all devices.
In chains using the PoS algorithm, transactions are added to blocks by validators — network participants who lock a certain amount of the network’s coins in their accounts. They do not need any special equipment, as the system automatically selects a validator to add a new block to the chain.
The coins locked on the validators’ accounts not only help to maintain the blockchain’s operation but also serve as a guarantee that the validator will perform their duties with integrity. In the event of deliberate or accidental inclusion of incorrect data, the validator may lose not only their reward but also their staked tokens.
About mining
So far, we have examined how new cryptocurrency units enter circulation and which types of blockchains support mining. Now it is time to take a closer look at what mining actually is and where it all began, especially considering that in the early days, mining could be done on a laptop without any specialized equipment.
The essence of mining lies in verifying the validity of transactions that are sent to the blockchain. To perform this verification, a series of complex calculations must be carried out and done faster than other participants. This requires powerful and expensive hardware.
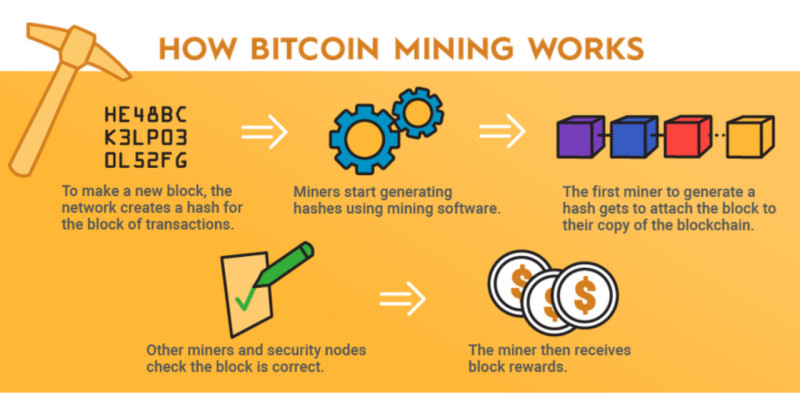
The core task involves finding a hash, a unique 64-character code into which the data is transformed. If the hash is computed correctly, the transaction is added to a block, and the block is then appended to the blockchain. The miner receives a reward for the completed work in the form of newly issued currency units; this is how additional coins enter circulation.
However, the primary purpose of mining is not just to issue coins but to verify and secure the network. It is this function that enables the blockchain to operate in a decentralized manner, without the need for intermediaries or third-party oversight. The high cost of mining equipment acts as a safeguard, making it prohibitively expensive for attackers to carry out a network breach, since doing so would require control over more than 51% of all devices.
Since the total number of digital coins that can enter circulation is limited, the difficulty of mining continuously increases, while the reward gradually decreases. In the case of Bitcoin, for example, the maximum number of coins is capped at 21 million units. Approximately 18 million have already been mined, but experts estimate that mining of the remaining coins will continue until around the year 2140.
This is due to the fact that the cryptocurrency's code includes an algorithm that automatically increases mining difficulty. At present, the average time required to add a new block is approximately 10 minutes. However, this difficulty level is recalculated automatically every two weeks. If the total computational power in the network increases, the mining difficulty is adjusted upward accordingly.
Mining: how it all began
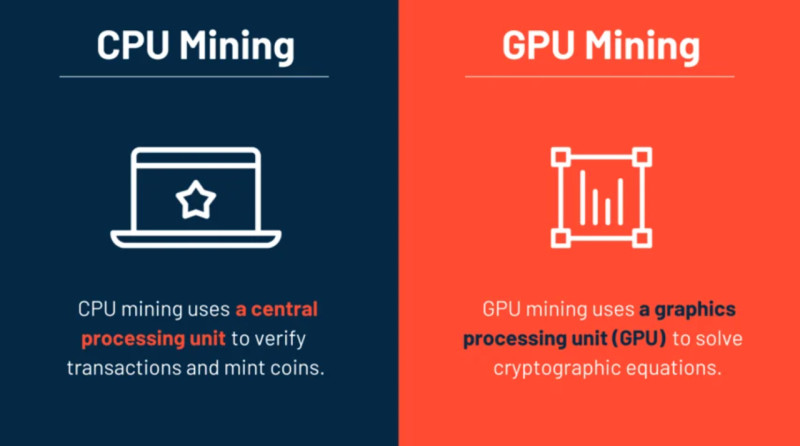
Initially, mining cryptocurrency did not require such powerful hardware as it does today, which is why any user could mine using the processor of a personal computer (CPU). This served the goal of decentralization, which has always been a core principle of digital currencies.
However, in the beginning, no one took cryptocurrency seriously, so people mined it merely for fun. Users were mining thousands of Bitcoins but had no idea what to do with them. At that time, coins could not be used to purchase anything, nor were they considered an investment, as this was an entirely new phenomenon.
There is a well-known story about one miner who posted an advertisement offering 10,000 Bitcoins to anyone who would order him two pizzas. Someone accepted the offer, and the transaction took place. These two pizzas later became known as the most expensive pizzas in history, as within a few years, the price of Bitcoin increased by several thousand times.
The first Bitcoin miner was its creator—a person or group of people under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, whose identity remains unknown to this day. As more and more processors joined the Bitcoin mining process, this triggered a mechanism that increases mining difficulty.
This algorithm was embedded in the cryptocurrency’s code and means that the more users participate in mining, the more difficult the process becomes for everyone. The first increase in mining difficulty occurred approximately one year after the initial block was mined, and within another six months, the difficulty had quadrupled.
This was due to the growing popularity of the first digital currency, which, in turn, led to an increase in its value and the possibility of earning real income. Gradually, mining began to shift toward a commercial foundation. It was taken up by companies using entirely different equipment.
Further stages of development
So, when a broader range of users, including commercial firms, became interested in mining digital currencies, they began to use more powerful hardware, which led to the emergence of GPU mining. This was a breakthrough in cryptocurrency mining, as these devices were significantly more powerful than CPUs.
Moreover, a single machine could be equipped with multiple graphics cards, each capable of calculating dozens of times more hashes than a processor. Thanks to this, entire mining farms and pools began to appear—we will discuss them in more detail a bit later.
The first mining farm was launched using a graphics processing unit (GPU), which offered a much higher computation speed. Additional processing power could be achieved by combining several graphics cards on a single motherboard.
For approximately three years, graphics cards dominated the mining market. At the same time, GPU-based systems require a substantial amount of electricity, constant attention, and additional expenses. Therefore, users began searching for more energy-efficient and cost-effective solutions.
This led to the introduction of FPGA chips for coin mining. These were not as versatile as CPUs but were significantly more energy-efficient. Like graphics cards, multiple FPGA chips could be used in a single device; however, such a device was more compact than a GPU-based mining farm.
At the same time, FPGA mining was significantly more expensive than previous GPU-based methods, which is why it never became widely accessible to the general public. However, the technologies used in their development were later applied in the creation and implementation of new, highly specialized chips called ASICs, which were designed to perform only one task.

Thus, ASIC miners emerged—devices capable of mining cryptocurrency at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, their cost was several times higher than any of the previously used devices. Several major companies entered the market to develop and produce such chips, the most well-known being ASICminer, Avalon, and Butterfly Labs.
Earnings from mining
When it comes to mining the first digital currency at the dawn of its emergence, Bitcoin mining was a highly profitable activity. On the one hand, it did not require powerful hardware; on the other, the reward was quite substantial. However, at the beginning, no one took this activity seriously, as there was little trust in cryptocurrency.
As previously mentioned, mining could initially be done solo without any special equipment. However, over time, more powerful and expensive hardware became necessary. In addition, the size of the reward for each mined block gradually began to decrease.
This process in the Bitcoin blockchain is called halving: the reward is reduced by half after a certain period of time, specifically every four years. The first halving occurred in 2012. Before this point, the reward was 50 Bitcoins per block; afterwards, it was reduced to 25 BTC.
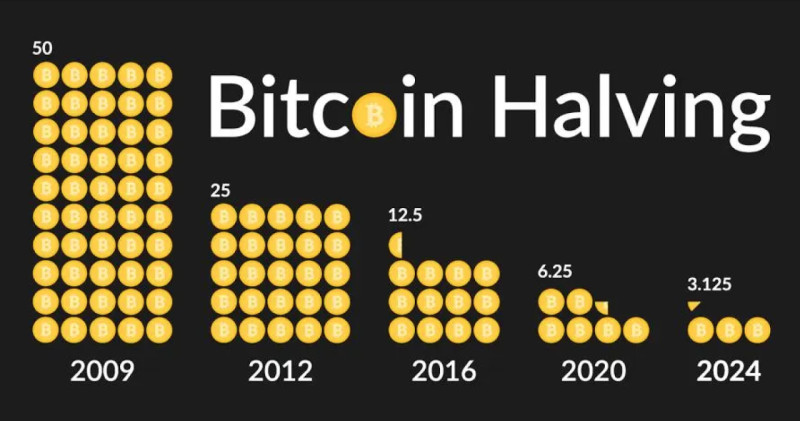
During the next halving in 2016, the reward dropped from 25 to 12.5 BTC, and in 2020, to 6.25 BTC. At present, another halving has already taken place, reducing the reward to just 3.125 BTC. It is expected that the final halving will occur in the year 2140, coinciding with the mining of the last Bitcoin.
It is worth noting that the gradual reduction of the reward is characteristic not only of Bitcoin but also of several other digital currencies that operate on the PoW (Proof of Work) mining algorithm. For example, in the Litecoin chain, the reward is halved every 840,000 blocks.
Thus, we have already explored the different mining methods and the types of equipment that have been and are being used. At present, the most effective devices for mining cryptocurrency are ASIC miners, as they offer the highest level of performance.
With such equipment, it is possible to earn between $500 and $1,000, depending on the chosen digital currency and the mining difficulty. For users who wish to earn more, it is possible to build a mining farm using these devices and generate an income of $3,000 to $5,000 per month. However, it is important not to overlook the rather high cost of the equipment itself.
Mining of other coins
In addition to Bitcoin, other digital currencies rely on the PoW algorithm for mining, one of which is the meme currency Dogecoin. Let us take a closer look at how Dogecoin mining and the mining of some other coins work, as well as how much one can earn from it.
As previously mentioned, the process of mining Bitcoin is continuously becoming more complex, and the reward for mining it is constantly decreasing. For this reason, users are looking for alternative ways to earn through mining: joining forces with other miners, setting up farms, or mining other cryptocurrencies.
The second-largest digital currency by market capitalization, Ethereum, initially also used the PoW mining algorithm. However, it was later decided to transition to the PoS algorithm. Now, new coins are added through staking: to receive new tokens, one must first purchase and stake a certain amount of the currency.
Still, among cryptocurrencies that have continued to use the PoW algorithm, there are several interesting options. Dogecoin is a meme coin that does not serve any practical purpose, yet it has gained widespread popularity due to Elon Musk’s support on social media. This currency consistently ranks in the top 10 cryptocurrencies.
The issuance of Dogecoin is unlimited, which means it can be mined endlessly. The reward for mining a new block is 10,000 units of the currency, and new blocks are added every minute (in the Bitcoin chain, this interval is no less than 10 minutes). Moreover, mining Dogecoin does not require hardware as powerful as that used for Bitcoin mining.
Litecoin is a fork of BTC, meaning it was created based on Bitcoin’s source code. It was developed as a complement to the first cryptocurrency, which is why many of its characteristics are similar. For example, Litecoin also undergoes halving, but its blocks are mined four times faster — that is, every 2.5 minutes.
Mining farms
As previously mentioned, the emergence of mining farms and miner collectives was primarily driven by the increasingly complex process of cryptocurrency mining, which made solo mining too difficult and costly. Let us take a closer look at what a mining farm is and how it operates.
A farm is a collection of multiple devices assembled for mining digital currencies. Mining farms can vary in appearance and configuration, but they all share one defining feature: they combine the computing power of a large number of devices, which results in high performance.
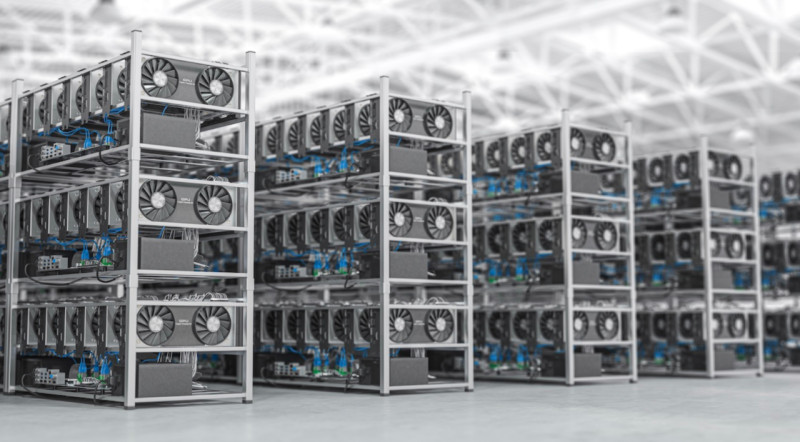

In general, every mining farm consists of several key components:
1. Hardware — This is the most essential part of any farm. It includes graphics cards, GPU units, or ASIC miners, i.e., devices that directly perform blockchain task-solving operations.
2. Cooling system — This consists of fans, air conditioners, and/or other devices. The need for cooling arises from the fact that farms consume large amounts of energy and, in turn, generate substantial heat. Without proper cooling, the hardware can overheat.
3. Software — This coordinates the operation of the entire farm and ensures its uninterrupted performance. The software used depends on the type of cryptocurrency being mined and the structure of the farm itself.
4. Internet connection — This is necessary for the synchronization and connection of the mining farm with the blockchain network, as well as for submitting newly mined blocks. To ensure a stable connection, server equipment is used, including servers, switches, and other devices.
5. Power supply system — This includes power units, distribution systems, and other specialized devices needed to deliver the high power output required to operate the farm.
6. Cables and connections — These link all the farm’s components together: miners, servers, power systems, and Internet access. Ergonomics and safety are key requirements for these elements.
Mining Pools
Building a mining farm with substantial computing power is a rather costly undertaking. For this reason, mining farms are typically established by commercial organizations rather than individual miners.
However, for those who want to try mining, for example, Ethereum, there are other options such as joining forces with other users in what are called mining pools. Unlike a farm, a pool is not a collection of hardware but rather a group of miners who collaborate to mine digital currencies together.
Each participant in the pool contributes the processing power of their devices to solve blockchain tasks. Once one of the pool members finds a valid solution, the reward is distributed among all participants in proportion to their contribution.
Joining a pool increases the chances of earning a reward while remaining more accessible and less expensive than building a mining farm. Let us take a closer look at how these mining collectives are organized and how they function.
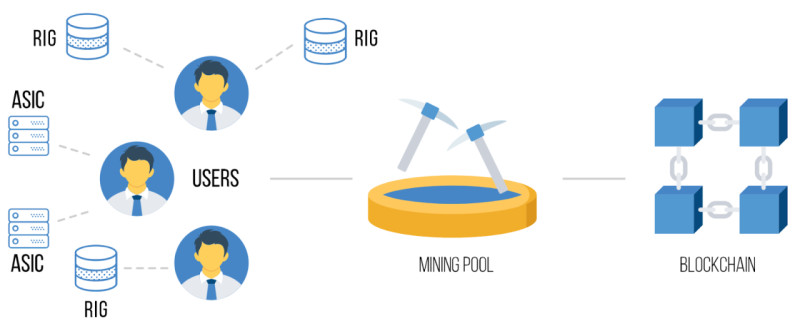
To become part of a pool, a user must install special software that enables communication with the pool’s server. This server is responsible for assigning tasks to participants. Each task is broken down into smaller units (shares), which are then processed individually by each participant’s device.
Once miners complete their assigned tasks, they send the results back to the server, which verifies the solutions and records each participant’s contribution. When the pool successfully adds a new block to the blockchain, it receives a reward consisting of a fixed block reward and the transaction fees included in that block.
It is important to note that this is precisely why miners prioritize transactions with higher fees. Since their rewards depend on these fees, they are directly motivated to process such transactions first.
As mentioned earlier, the total reward is divided among pool participants in proportion to the amount of work each has contributed. There are different payout models, and each pool determines the method by which the earned reward is distributed.
Cloud mining
We have already discussed in detail how and how much one can earn from mining digital currencies, but all of these methods require the purchase of expensive equipment. What should one do if there is no starting capital or if it is insufficient? For beginners, the solution may be cloud mining.
The main difference and advantage of cloud mining compared to other forms of this activity is that there is no need to purchase one’s costly equipment. Coin mining is carried out using rented equipment provided by large data centers.
Cloud mining has another significant advantage: there is no need to monitor the technical condition of the equipment, perform maintenance, which would otherwise require additional time and financial resources, or pay electricity bills. All of these responsibilities rest with the equipment owner.
The benefits for service providers are obvious: data centers can receive a fixed and regular income from long-term rentals. As for miners, the arrangement is also profitable, as they can select equipment with the required specifications for mining their chosen currencies.
The user can either diversify by allocating capacity to mine several types of currencies or increase the mining volume of one currency they consider most promising by expanding capacity. However, despite its appeal, cloud mining has several drawbacks:
- High rental costs – Provider tariffs, including commissions, can be comparable to mining on one’s own equipment, with the only difference being that the user does not actually own the equipment.
- No resale option – When a user purchases their own equipment, they can later resell it, thereby offsetting part of their expenses. In cloud mining, the user does not own the equipment and therefore cannot resell it.
- Minimum withdrawal limits – Some services set withdrawal thresholds and do not allow funds to be transferred until a certain amount of coins has been accumulated in the wallet.
- Hacker attacks – Large services attract cybercriminals who can gain control of users’ wallets and steal their mined digital coins.
- Fraud risk – The greatest danger in cloud services. All operations between the service provider and the miner take place online, which can make it difficult to determine whether the provider genuinely offers such services or whether the entire operation is a scam.
Hidden mining
Sometimes one can become involved in mining even against one’s will. This is because cybercriminals can remotely connect to other users’ personal computers and use their processing power to mine cryptocurrency. This is known as a mining virus. In this section, we will explain how to recognize such threats and how to combat them.
Infection of computers with any type of virus leads to a deterioration in performance, or, in simple terms, causes the system to “freeze.” Since 2018, specific viruses have emerged that use other people’s computers for cryptocurrency mining. Initially, such programs employed malicious code to download and run an executable file on devices targeted by criminals.
However, recently, another form of criminal activity has gained popularity—cryptojacking, which enables cryptocurrency mining through a simple JavaScript. This means that malicious actions can be carried out directly in the user’s browser without the need to install any special software.
Mining viruses utilize the resources of victims’ computers to mine digital coins, which are subsequently transferred to the wallets of the attackers. The greatest danger lies in the fact that they cause overheating and rapid wear of computer components due to excessive load.
The first to fail are those components that can be involved in mining: video cards, RAM, processors, and cooling systems. The strain on these systems causes the equipment to slow down and fail to cope with the user’s other tasks.
In addition, such programs may collect various information about the device owner, as well as steal photographs, files stored on the device, and registration details from various accounts. This, in turn, can lead to data loss and, in some cases, even to financial losses.
A computer can be infected with a virus in two main ways: by downloading files from suspicious sources or by opening emails that end up in the “spam” folder. These programs can be detected using antivirus software with updated databases, although even then, they are often only able to identify the simplest viruses.
Malicious programs can be removed using antivirus software or manually. For protection, it is necessary to avoid downloading suspicious files and visiting dubious websites. It is also recommended to use special browser extensions.
Mining on smartphone
We have already discussed in detail how energy-intensive the process of cryptocurrency mining can be and what kind of equipment it requires. Nevertheless, some users attempt to mine using a mobile phone. Let us examine whether this is possible and what profit, if any, can be expected.
It should be noted that major smartphone manufacturers (such as Apple) banned mining on their devices as early as 2018. This is because cryptocurrency mining places a heavy load on devices, leading to damage: the processor fails, and the battery discharges quickly.
At the same time, cloud mining is permitted by manufacturers, and applications for it are available for free download from app stores (App Store or Play Market). This is because cloud mining does not use the resources of the device itself and is, arguably, the only viable option for mining cryptocurrency on a phone.
Thus, all that is required to start mining on a mobile phone is to download an application. However, one should exercise caution to avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes: if an application requires access to a bank card or personal data, this should raise immediate concern.
After downloading suspicious applications, the device may start to operate more slowly or overheat. This is a strong indication that, along with the program, the user may have downloaded a virus, or the device has been hacked by cybercriminals.
Although the costs of mining digital currencies on a phone are virtually nonexistent, one should not expect substantial profits either, as mobile devices do not have sufficient processing power. In most cases, the income amounts to mere pennies, which means there is little practical sense in mining with a phone.
How to start
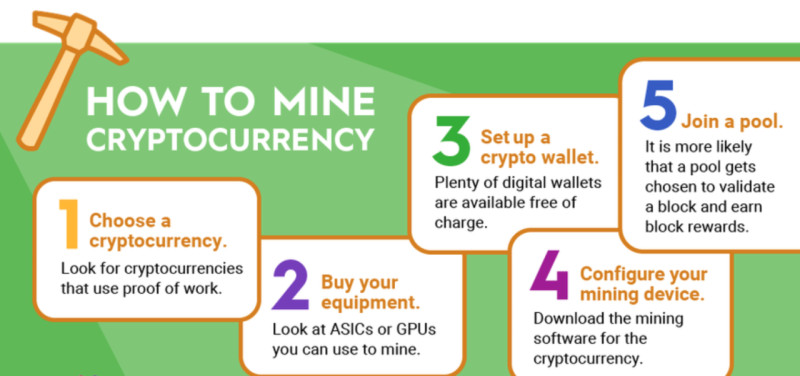
As we have already seen, starting cryptocurrency mining does not necessarily require huge initial investments. However, before beginning, it is essential to determine the most important aspects for yourself: which specific currency to mine, whether to do it independently or as part of a pool, and so on.
The first step is to decide on the coin or coins you plan to mine. This choice will determine the type of equipment required, as well as whether the miner will need to join a mining pool or can mine independently.
Once you have selected a specific crypto asset, you can proceed to prepare the equipment. As discussed earlier, mining may require cheaper but less powerful graphics cards or ASIC miners, which are more productive but also more expensive.
In addition, it is necessary to install special software (for example, Cudo Miner or Kryptex Miner). These programs run in the background, using all the computer’s free resources to mine cryptocurrency. If mining is prioritised, the computer will operate more slowly.
Specialised mining devices can be purchased on the secondary market at a significantly lower price. If buying, configuring, and maintaining the equipment, including its technical servicing, seems too complex, cloud mining can be considered, as it does not require such equipment.
It is important to understand that investing capital in mining equipment carries significant risks. Such devices can rarely be used for other purposes, so if mining stops generating profit, selling them will be nearly impossible.
Moreover, electricity costs often exceed the potential profit from mining. This is only beneficial for those who can purchase electricity at discounted rates. However, in some countries, governments seek to increase, rather than reduce, electricity prices for miners.
It is also worth considering that public concern over the negative environmental impact of mining has led to mining bans in some countries, as happened in China. As a result, modern digital currencies increasingly use another, more environmentally friendly consensus algorithm—Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Conclusion
In this article, we have examined what mining is, its key aspects, and the main ways to obtain digital currencies. Cryptocurrencies are not issued by any central authority, unlike fiat money, and they can be obtained in two main ways: by purchase or by mining.
Mining algorithms differ depending on the blockchain structure. In Proof-of-Work (PoW) networks, new currency units enter circulation through mining; in Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chains, through staking. Mining involves solving complex mathematical problems, while staking involves locking coins in one’s account.
Both methods result in receiving rewards in the form of new currency units. However, cryptocurrency mining is becoming increasingly complex, and the size of the reward is gradually decreasing. As a result, solo mining is becoming too expensive and often unprofitable.
To increase power, mining farms are created, but this method is practically inaccessible to solo miners due to the high cost of equipment. Therefore, users join mining pools for joint mining or turn to cloud mining, which does not require purchasing their equipment.
To begin cryptocurrency mining, the first step is to select a specific currency, as this will determine the mining method, the necessary equipment, and the potential income. Many users focus solely on Bitcoin mining, but many other currencies are much easier and more profitable to mine.








 Back to articles
Back to articles



